Table of Contents
Introduction to Strong Encryption
Strong Encryption is a vital tool in today’s digital age, where virtually every aspect of our lives is connected to the internet, online surveillance has become a pervasive concern. Governments, corporations, and malicious actors have the capability to monitor, track, and analyze our online activities, often without our knowledge or consent. This invasion of privacy has raised significant ethical and security issues, making it essential for individuals to take proactive measures to protect their personal information. One of the most effective tools available for safeguarding online privacy is strong encryption.
Source: Archive.org
Understanding Strong Encryption
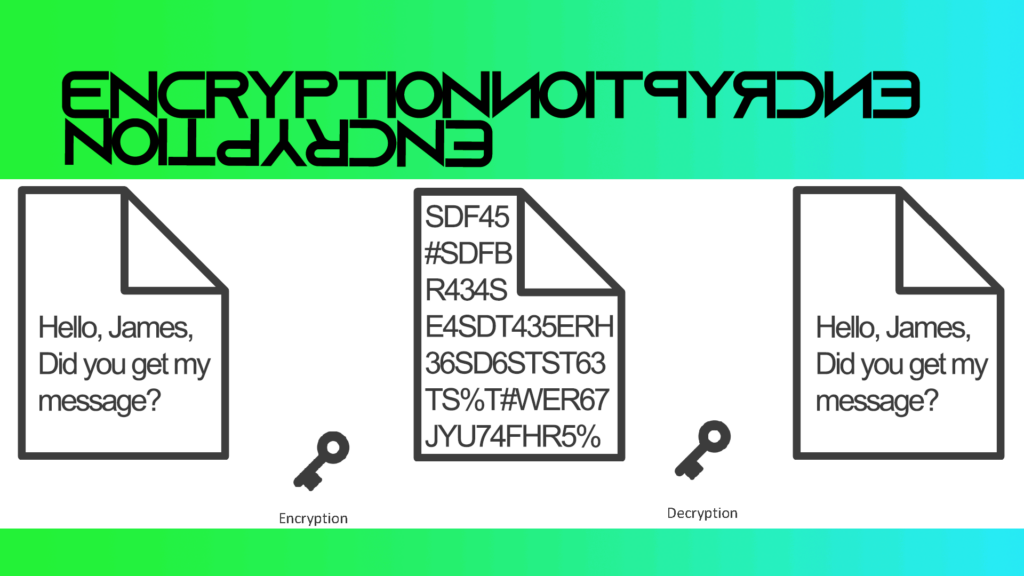
Strong encryption is the process of converting plain text into a coded format that is unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted by unauthorized parties, it remains unintelligible. There are two primary types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys—one public and one private. Both methods play crucial roles in securing digital communications and data.
The Importance of Strong Encryption
Strong encryption refers to the use of robust cryptographic algorithms and longer key lengths to ensure the highest level of security. The strength of encryption is measured by how difficult it is for an unauthorized party to break the code. Weak encryption can be easily cracked, exposing sensitive information to potential threats. Therefore, employing strong encryption is vital for protecting against sophisticated surveillance techniques.
Avoiding Government and Corporate Surveillance
Governments around the world engage in various forms of surveillance, often justified by national security and law enforcement purposes. However, these practices can lead to significant breaches of personal privacy. For example, programs like the NSA’s PRISM have demonstrated how governmental bodies can collect and analyze vast amounts of data from unsuspecting citizens. Similarly, corporations track user behavior to build detailed profiles for targeted advertising, which can also lead to privacy invasions.
Strong encryption acts as a shield against such surveillance by making it extremely challenging for unauthorized entities to access private communications and data. By encrypting emails, messages, and other forms of digital communication, individuals can ensure that their conversations remain confidential. Additionally, using encrypted storage solutions protects files and documents from unauthorized access.
Protecting Against Cybercriminals
Online surveillance is not limited to government and corporate entities; cybercriminals also pose a significant threat to personal privacy. These malicious actors employ various tactics, such as man-in-the-middle attacks, phishing, and data breaches, to intercept and steal sensitive information. Strong encryption is a critical defense mechanism against these threats.
For instance, encrypted connections (HTTPS) protect data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website, preventing attackers from eavesdropping on the communication. Similarly, end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in messaging apps ensures that only the communicating parties can read the messages, rendering intercepted data useless to cybercriminals.
Implementing Strong Encryption
Implementing strong encryption in everyday digital activities is not as daunting as it may seem. Here are five practical steps individuals can take to enhance their online privacy:
- Use Encrypted Communication Tools: Opt for messaging apps that offer end-to-end encryption, such as Signal, WhatsApp, or Telegram. For email, consider providers that prioritize encryption, like Proton Mail or Tutanota.
- Enable HTTPS Everywhere: Ensure that your web browsing is secure by using HTTPS connections. Browser extensions like HTTPS Everywhere can automatically enforce secure connections to websites.
- Encrypt Your Devices: Enable encryption on your smartphones, tablets, and computers. Both iOS and Android devices offer built-in encryption options, and operating systems like Windows and macOS provide disk encryption tools (BitLocker and FileVault, respectively).
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet connection, making it difficult for third parties to monitor your online activities. Choose reputable VPN providers such as Proton VPN that do not abuse user data.
- Secure Cloud Storage: When using cloud storage services, opt for providers that offer client-side encryption, meaning files are encrypted before being uploaded. Examples include Tresorit and Sync.com.
The Future of Strong Encryption
As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods of surveillance and cyber-attacks. This ongoing arms race underscores the importance of advancing encryption technologies. Quantum computing, for example, poses a potential threat to current encryption standards. However, researchers are already developing quantum-resistant algorithms to address this challenge.
In conclusion, strong encryption is an essential tool for preserving online privacy and avoiding surveillance. By implementing robust encryption practices, individuals can take control of their digital lives and protect themselves from unauthorized access. As the digital landscape continues to change, staying informed about the latest encryption technologies and best practices will remain crucial in the fight for privacy.
The PRISM program, among other revelations, has shown us the extent to which surveillance can intrude upon personal privacy. Using strong encryption ensures that your data remains private and secure, providing peace of mind in an increasingly interconnected world. By taking the steps outlined above, you can shield your privacy and enjoy the benefits of a secure digital environment.
References
- Kaspersky – What is Encryption?
- NIST – Encryption Basics
- TechTarget – Strong Encryption
- Electronic Frontier Foundation – NSA’s PRISM
- Privacy International – Corporate Surveillance
- ProtonMail – Why Encryption Matters
- Guardian – Surveillance and Privacy
- HTTPS Everywhere
- Signal – End-to-End Encryption
- WhatsApp – Security
- Telegram – Secret Chats
- ProtonMail – Secure Email
- Tutanota – Encrypted Email
- Apple – iOS Security
- Microsoft – BitLocker
- Apple – FileVault
- NordVPN – VPN Guide
- ExpressVPN – How VPNs Work
- Tresorit – Secure Cloud Storage
- Sync.com – End-to-End Encryption

